Pulmonary embolism (PE)
it is not complete but do include key points that we need to know to work in ward.
pathophysio:
- it results from DVT - venous thromboembolism
- venous stasis, endothelial injury and hypercoagulability.
bridging:
- egfr>30: s/c clexane BD
- egFR 15-30 - s/c clexane OD
- eGFR <15 - IVI heparin (kena monitor coag 6 hourly)
- Warfarin affects the APTT & PT value
- Clexane - APTT (to help INR reaches the aim faster)
- Aim INR 2-3, once INR >2, off clexane, bridging complete
4th day start adjusting dose base on INR
- pharmacist has special counsellor or booklet for the patient to understand the use of warfarin. with constant follow up and also diet suggestions (no green leafy veges)
look for ST changes S1Q3T3
- deep S wave in lead I, Q wave in lead 3, T inversion in lead 3
- ST depression, RBBB
- P. pulmonale
2. blood Ix: trop t and ck stat
3. basic supportive tx: HFM, transfer to acute bed
request for :
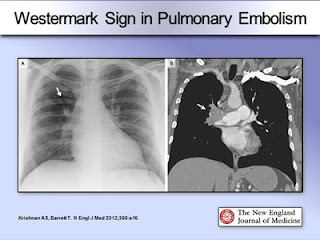
- CXR : hamptoms hump: wedgemark sign, westermark sign: pulmonary oligaemia in the affected segment
- for those who have clot in the past, and have a previous episode before, or those who has acute kidney damage/ckd.
- clear cxr
- ultrasound for lower limb: to rule out lower limb DVT due to long sitting/surgery...
- start DAPT
4. echo:
- look for RV dilation and hypokinesia. - acute rv failure--> increase afterload, rv cannot unload sufficiently causing rv dilated. impinge on LV cause LV to decrease output and supply to CA
- it increases o2 demand which CA could not meet, results in ischemia and necrosis
- it increases o2 demand which CA could not meet, results in ischemia and necrosis
MASSIVE PE:
HYPOTENSION BP<50 for at least >15MINUTES, HR <40 - usually with evidence of MI and hyocardial dysfunction
Well's score for PE
low<2, mid 2-6, high >6
1. clinical signs of DVT -3
2. previous surgery / long traveeling>4hrs -1.5
3. previous DVT and PE- 1.5
4. HR>100 - 1.5
5. other diagnosis seem less likely -3
6.hemoptysis -1
7. cancer -1
1. clinical signs of DVT -3
2. previous surgery / long traveeling>4hrs -1.5
3. previous DVT and PE- 1.5
4. HR>100 - 1.5
5. other diagnosis seem less likely -3
6.hemoptysis -1
7. cancer -1
- without hypotension: LWMH, fonda/ DOACS- unstable/ bleeding: parental anticoag 5-10d, switch to warfarin overlap 3-7d before discontinue heparin when INR >2 for >2d- continue anticoag for 3-6months
thrombolytic therapy:
STK 25mu if pt high risk massive PE/ with cardiopulmonary arrest.
other mx:
1. rivaroxaban 15mg BD for 21d then 20mg OD2. dabigatran (expensive)
Reference:







No comments:
Post a Comment