Heart Failure(HF)
1. intro
2. pathophysio
3. Signs and Symptoms
4. Classifications: NYHA
5. Investigations
6. Management
HF is a structural or physiological abnormality of the heart resulting in its inability to meet the metabolic demands of the body or its ability to do so only at higher than normal filling pressure
Population:
EF <40% HFrEF
EF>50% HRpEF
EF: 40-50: HFmrEF
Pathophysio
Acute heart failure Signs and Symtoms
4 types of symptoms to show which type of HF belongs to.
- warm and wet: adequate perfusion but congested (lungs/peripheral) - volume overload
- cold and dry - hypoperfuse, dehydrated - pump failure
- cold and wet - hypoperfuse and congested
- ward and dry - adequate perfusion and dehydrated - mild HF/ compensated stage of HF
what is reperfusion? The restoration of blood back into tissue
- Elevated jugular venous pressure
- is a manifestation of abnormal right heart dynamics, mostly commonly reflecting elevated pulmonary capillary wedge pressure from left heart failure. This usually implies fluid overload, indicating the need for diuresis.
Left and Right sided heart failure differences:

NYHA:
I- no limitation ,
II: slight limitation, comfortable at rest, activity causes fatigue
III: dmarked limitation: less than ordinary activity causes sx
IV: unable to carry out physical activity without discomfort.
Imvestigations (Ix):
- ECG
- - access HR, rhythm,
- QRS morphology /durarion/voltage,
- evidence of ischemia, LVhypertrophy/ arrthymia
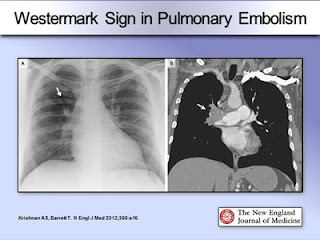
- chest radiography:
- pulmonary congestion, cardiomegaly , or other lung pathology
- Echo
- to determine type of HF- assess LV chamber size, thicknesss- diastolic fxmyocardial ischemia test: treadmill exercise, stress echocardio,
- invasive:
- coronary angiography
- others: holter, pulmonary function test
- FBC
- RP
- LFT
- CBS
- FLP
- HbA1c
- Natiuretic Peptides/BNP:
- peptide hormones synthesized by the heart, brain and other organs. to reduce arterial pressure by decreasing blood volume and systemic vascular resistance
- the higher the number= heart could not pump the way it should- release when cardiac myocytes are strained- useful to rule out acute dypsnea- NP can increase also when pt have AF/ CRF/ age/ obese/ ARNI- significant if >400, age >50: >450, age 50-75 :>900, age>75: >1800
- CK:
- inflammation of muscle, indicates level of damage or disease of skeletal muscle
- TFT
- infective screening
- iron study,
- - to check Tsat: Fe/TIBC x100, if <20% : inadequate iron supply
- urine test: UFEME/ C+S
- blood gas:
- hypoxemia: paO2<60- hypercapnia: PaCO2>50- Acidosis: pH<7.35
Management(Mx):
- stabilise hemodynamics
- maintain o2 and perfusion of organs
- relieve symptoms and signs
- treat u/l cause or aggravating factors
1. non pharma, pharma
- Diuretics
- ACEI
- ARB
- Beta blockers
- MRA
- Statins
2. Surgery3. Device therapy- catheter ablation/pacemaker therapy
Common drugs used:
- dopamine: improve renal perfusion and promote diuresis / increase BP
- dobutamine: peripheral hypoperfusion n pulmonary congestion
- Ivabradine: slows the heart rate to allow more perfusion to the heart
- thiazides: hydrochlorothiazides: promote natiuresis and diuresis
To watch out for
- worsen symptoms, readmission rate
- increase in cardiovascular event rate
- increase in bleeding risk and stroke rate
- adverse effects due to pharmacotherapy
1. Malaysia CPG for HF